PAT A1053 Path of Equal Weight (30分) (DFS深度优先搜索+剪枝)
条评论PAT甲级:A1053 Path of Equal Weight (30分)
Given a non-empty tree with root R, and with weight Wi assigned to each tree node Ti. The weight of a path from R to L is defined to be the sum of the weights of all the nodes along the path from R to any leaf node L.
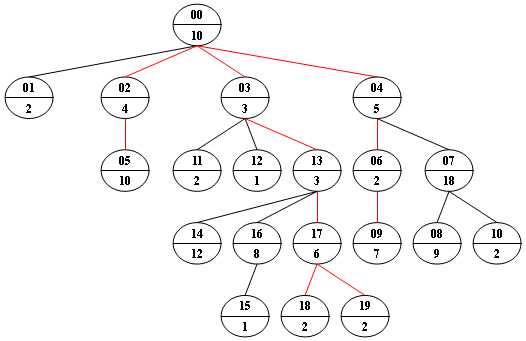
Now given any weighted tree, you are supposed to find all the paths with their weights equal to a given number. For example, let’s consider the tree showed in the following figure: for each node, the upper number is the node ID which is a two-digit number, and the lower number is the weight of that node. Suppose that the given number is 24, then there exists 4 different paths which have the same given weight: {10 5 2 7}, {10 4 10}, {10 3 3 6 2} and {10 3 3 6 2}, which correspond to the red edges in the figure.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing 0<N≤100, the number of nodes in a tree, M (<N), the number of non-leaf nodes, and 0<S<230, the given weight number. The next line contains N positive numbers where Wi (<1000) corresponds to the tree node Ti. Then M lines follow, each in the format:
1 | ID K ID[1] ID[2] ... ID[K] |
where ID is a two-digit number representing a given non-leaf node, K is the number of its children, followed by a sequence of two-digit ID‘s of its children. For the sake of simplicity, let us fix the root ID to be 00.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print all the paths with weight S in non-increasing order. Each path occupies a line with printed weights from the root to the leaf in order. All the numbers must be separated by a space with no extra space at the end of the line.
Note: sequence {A1,A2,⋯,An} is said to be greater than sequence {B1,B2,⋯,Bm} if there exists 1≤k<min{n,m} such that Ai=Bi for i=1,⋯,k, and Ak+1>Bk+1.
Sample Input:
1 | 20 9 24 |
Sample Output:
1 | 10 5 2 7 |
- 题意:给出一棵树,树中每个结点包含编号和权值,编号从 0~N,要求输出从根节点到某一叶子结点路径上各结点的权值(要求这条路径上的权值和等于给定的 W ),如果有多条路径满足条件,则按照降序输出各个路径,例如 a = [10, 5, 2],b = [10, 4, 9],则说 a > b,因为第二项中 5 > 4。
- 分析:其实考察的就是DFS,每个结点有两个属性,所以定义一个结构体数组,每个元素包含其权值和孩子结点的编号。因为要求降序输出,可以在读入孩子结点的时候就按照其权值降序排序。之后在DFS中传入结点编号 u 与当前权值和 sum 两个属性,如果 sum大于W 或者 sum等于W但当前结点不是叶子结点则退出(剪枝),如果满足条件则直接输出当前路径的权值。另一种方式则是先记录下所有满足条件的路径,之后再一起输出。
方法一:(剪枝回溯)
1 |
|
方法二:(记录所有结果再行输出)
1 |
|
- 本文链接:https://blog.charjin.top/2020/02/16/pat-A1053/
- 版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 CN 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
分享