7-3 Postfix Expression 答案正确 得分: 25 / 25
Given a syntax tree (binary), you are supposed to output the corresponding postfix expression, with parentheses reflecting the precedences of the operators.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N ( 20) which is the total number of nodes in the syntax tree. Then N lines follow, each gives the information of a node (the -th line corresponds to the -th node) in the format:
data left_child right_child
where data is a string of no more than 10 characters, left_child and right_child are the indices of this node's left and right children, respectively. The nodes are indexed from 1 to N. The NULL link is represented by . The figures 1 and 2 correspond to the samples 1 and 2, respectively.
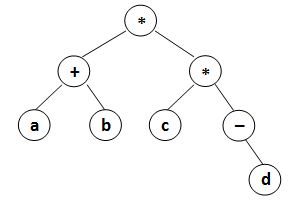 |
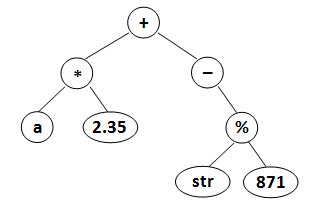 |
|---|---|
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 |
Output Specification:
For each case, print in a line the postfix expression, with parentheses reflecting the precedences of the operators.There must be no space between any symbols.
Sample Input 1:
8
* 8 7
a -1 -1
* 4 1
+ 2 5
b -1 -1
d -1 -1
- -1 6
c -1 -1
Sample Output 1:
(((a)(b)+)((c)(-(d))*)*)
Sample Input 2:
8
2.35 -1 -1
* 6 1
- -1 4
% 7 8
+ 2 3
a -1 -1
str -1 -1
871 -1 -1
Sample Output 2:
(((a)(2.35)*)(-((str)(871)%))+)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 25;
bool vis[maxn];
struct node {
string v;
int lc, rc;
} Node[maxn];
int n;
bool isOperator(string str) {
return str == "-" || str == "/" || str == "*" || str == "+";
}
void postOrder(int root) {
if (root == -1) return;
cout << "(";
postOrder(Node[root].lc);
if (isOperator(Node[root].v) && Node[root].lc == -1) {
cout << Node[root].v;
postOrder(Node[root].rc);
} else {
postOrder(Node[root].rc);
cout << Node[root].v;
}
cout << ")";
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> Node[i].v >> Node[i].lc >> Node[i].rc;
if (Node[i].lc != -1) vis[Node[i].lc] = true;
if (Node[i].rc != -1) vis[Node[i].rc] = true;
}
int R;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i]) {
R = i;
break;
}
}
postOrder(R);
return 0;
}
| 测试点 | 结果 | 耗时 | 内存 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 答案正确 | 2 ms | 384KB |
| 1 | 答案正确 | 3 ms | 356KB |
| 2 | 答案正确 | 2 ms | 384KB |
| 3 | 答案正确 | 2 ms | 512KB |
| 4 | 答案正确 | 2 ms | 384KB |